
Download Links
 Download Catalog Download Catalog |
 Download Manual Download Manual |
 Download Hardware Manual Download Hardware Manual |
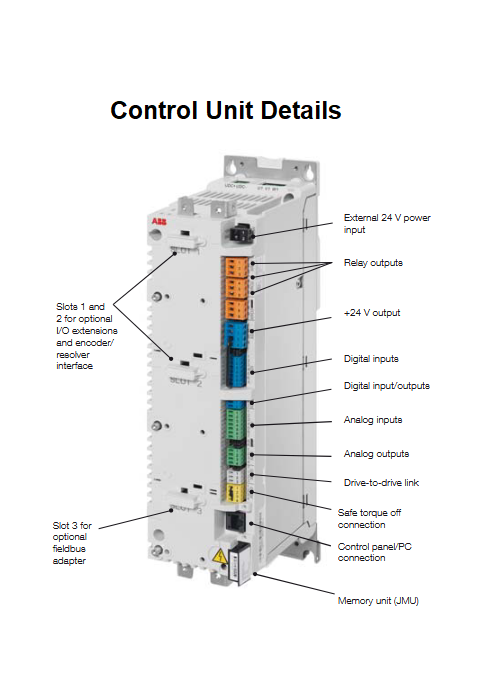
Wiring Details
Below image show terminal details:
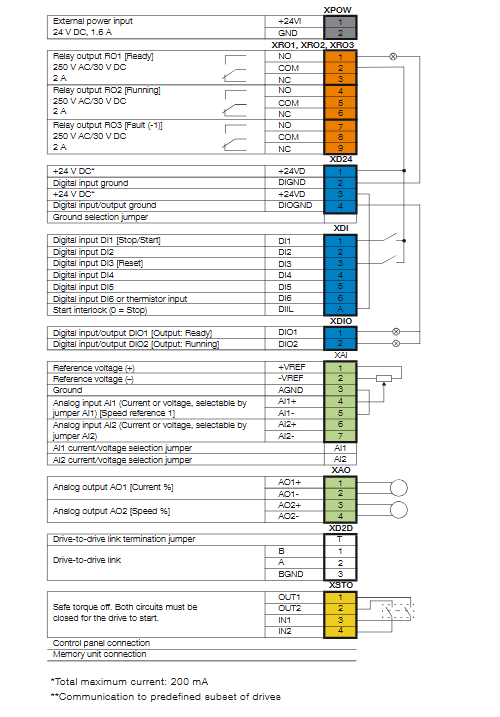
Faults & Alarms
Search from below list for ACS850 drive faults & alarms:
| Fault Code | Cause & Solution |
|---|---|
| A2000 BRAKE START TORQUE | Cause: Mechanical brake alarm. Alarm is activated if required motor starting torque (42.08 Brake open torq) is not achieved. Solution: 1. Check brake open torque setting, parameter 42.08. 2. Check drive torque and current limits. 3. See parameter group 20 Limits. 4. This is a Programmable fault also: check parameter 42.12 Brake fault function. |
| A2001 BRAKE NOT CLOSED | Cause: Mechanical brake control alarm. Alarm is activated e.g. if brake acknowledgement is not as expected during brake closing. Solution: 1. Check mechanical brake connection. 2. Check mechanical brake settings in parameter group 42 Mech brake ctrl. 3. To determine whether problem is with acknowledgement signal or brake, check if brake is closed or open. 4. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 42.12 Brake fault function. |
| A2002 BRAKE NOT OPEN | Cause: Mechanical brake control alarm. Alarm is activated e.g. if brake acknowledgement is not as expected during brake opening. Solution: 1. Check mechanical brake connection. 2. Check mechanical brake settings in parameter group 42 Mech brake ctrl. 3. To determine whether problem is with acknowledgement signal or brake, check if brake is closed or open. 4. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 42.12 Brake fault function. |
| A2003 SAFE TORQUE OFF | Cause: Safe Torque Off function is active, i.e. safety circuit signal(s) connected to connector X6 is lost while drive is stopped and parameter 30.07 Sto diagnostic is set to Alarm. Solution: 1. Check safety circuit connections. |
| A2004 STO MODE CHANGE | Cause: Error in changing Safe Torque Off supervision, i.e. parameter 30.07 Sto diagnostic setting could not be changed to value Alarm. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| A2005 MOTOR TEMPERATURE | Cause: Estimated motor temperature (based on motor thermal model) has exceeded alarm limit defined by parameter 31.03 Mot temp1 almLim. Solution: 1. Check motor ratings and load. 2. Let motor cool down. 3. Ensure proper motor cooling: Check cooling fan, clean cooling surfaces, etc. Check value of alarm limit. Cause: Measured motor temperature has exceeded alarm limit defined by parameter 31.03 Mot temp1 almLim. Solution: 1. Check motor ratings and load. 2. Let motor cool down. 3. Ensure proper motor cooling: Check cooling fan, clean cooling surfaces, etc. 4. Check that actual number of sensors corresponds to value set by parameter 31.02 Mot temp1 src. |
| A2006 EMERGENCY OFF | Cause: Drive has received emergency OFF2 command. Solution: To restart drive, activate Run enable signal (source selected by parameter 10.11 Run enable) and start drive. |
| A2007 RUN ENABLE | Cause: No Run enable signal is received. Solution: 1. Check setting of parameter 10.11 Run enable. 2. Switch signal on (e.g. in the fieldbus Control Word) or check wiring of selected source. |
| A2008 ID-RUN | Cause: Motor identification run is on. Solution: This alarm belongs to normal start-up procedure. Wait until drive indicates that motor identification is completed. Cause: Motor identification is required. Solution: This alarm belongs to normal start-up procedure. Select how motor identification should be performed, parameter 99.13 Idrun mode. Start identification routines by pressing Start key. |
| A2009 EMERGENCY STOP | Cause: Drive has received emergency stop command (OFF1/OFF3). Solution: 1. Check that it is safe to continue operation. 2. Return emergency stop push button to normal position (or adjust the fieldbus Control Word accordingly). 3. Restart drive. |
| A2011 BR OVERHEAT | Cause: Brake resistor temperature has exceeded alarm limit defined by parameter 48.07 Br temp alarmlim. Solution: 1. Stop drive. 2. Let resistor cool down. 3. Check resistor overload protection function settings (parameters 48.01…48.05). 4. Check alarm limit setting, parameter 48.07 Br temp alarmlim. 5. Check that braking cycle meets allowed limits. |
| A2012 BC OVERHEAT | Cause: Brake chopper IGBT temperature has exceeded internal alarm limit. Solution: 1. Let chopper cool down. 2. Check resistor overload protection function settings (parameters 48.01…48.05). 3. Check that braking cycle meets allowed limits. 4. Check that drive supply AC voltage is not excessive. |
A2013 DEVICE OVERTEMP | Cause: Measured drive temperature has exceeded internal alarm limit. Solution: 1. Check ambient conditions. 2. Check air flow and fan operation. 3. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 4. Check motor power against unit power. |
| A2014 INTBOARD OVERTEMP | Cause: Interface board (between power unit and control unit) temperature has exceeded internal alarm limit. Solution: 1. Let drive cool down. |
| A2015 BC MOD OVERTEMP | Cause: Input bridge or brake chopper temperature has exceeded internal alarm limit. Solution: 1. Let drive cool down. |
| A2016 IGBT OVERTEMP | Cause: Drive temperature based on thermal model has exceeded internal alarm limit. Solution: 1. Check ambient conditions. 2. Check air flow and fan operation. 3. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 4. Check motor power against unit power. |
| A2017 FIELDBUS COMM | Cause: Cyclical communication between drive and fieldbus adapter module or between PLC and fieldbus adapter module is lost. Solution: 1. Check status of fieldbus communication. 2. Check settings of parameter group 50 Fieldbus. 3. Check cable connections. 4. Check if communication master is able to communicate. 5. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 50.02 Comm loss function. |
| A2018 LOCAL CTRL LOSS | Cause: Control panel or PC tool selected as active control location for drive has ceased communicating. Solution: 1. Check PC tool or control panel connection. 2. Check control panel connector. 3. Replace control panel in mounting platform. 4. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 30.03 Local ctrl loss. |
| A2019 AI SUPERVISION | Cause: An analogue input has reached limit defined by parameter 13.33 AI superv cw. Solution: 1. Check analogue input source and connections. 2. Check analogue input minimum and maximum limit settings. 3. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 13.32 AI superv function. |
A2020 FB PAR CONF | Cause: The drive does not have a functionality requested by PLC, or requested functionality has not been activated. Solution: 1. Check PLC programming. 2. Check settings of parameter group 50 Fieldbus. |
| A2021 NO MOTOR DATA | Cause: Parameters in group 99 have not been set. Solution: 1. Check that all the required parameters in group 99 have been set. |
| A2022 ENCODER 1 FAILURE | Cause: Encoder 1 has been activated by parameter but the encoder interface (FEN-xx) cannot be found. Solution: 1. Check parameter 90.01 Encoder 1 sel setting corresponds to actual encoder interface 1 (FEN-xx) installed in drive Slot 1/2 (parameter 09.20 Option slot1 / 09.21 Option slot2). Note: The new setting will only take effect after parameter 90.10 Enc par refresh is used or after the JCU Control Unit is powered up the next time. |
| A2023 ENCODER 2 FAILURE | Cause: Encoder 2 has been activated by parameter but the encoder interface (FEN-xx) cannot be found. Solution: 1. Check parameter 90.02 Encoder 2 sel setting corresponds to actual encoder interface 1 (FEN-xx) installed in drive Slot 1/2 (parameter 09.20 Option slot1 / 09.21 Option slot2). Note: The new setting will only take effect after parameter 90.10 Enc par refresh is used or after the JCU Control Unit is powered up the next time. |
| A2027 FEN TEMP MEAS FAILURE | Cause: Error in temperature measurement when temperature sensor (KTY or PTC) connected to encoder interface FEN-xx is used. Error in temperature measurement when KTY sensor connected to encoder interface FEN-01 is used. Solution: 1. Check that parameter 31.02 Mot temp1 src / 31.06 Mot temp2 src setting corresponds to actual encoder interface installation (09.20 Option slot1 / 09.21 Option slot2): 2. If one FEN-xx module is used: – Parameter 31.02 Mot temp1 src / 31.06 Mot temp2 src must be set either to KTY 1st FEN or PTC 1st FEN. The FEN-xx module can be in either Slot 1 or Slot 2. 3. If two FEN-xx modules are used: – When parameter 31.02 Mot temp1 src / 31.06 Mot temp2 src is set to KTY 1st FEN or PTC 1st FEN, the encoder installed in drive Slot 1 is used. – When parameter 31.02 Mot temp1 src / 31.06 Mot temp2 src is set to KTY 2nd FEN or PTC 2nd FEN, the encoder installed in drive Slot 2 is used. 4. FEN-01 does not support temperature measurement with KTY sensor. Use PTC sensor or other encoder interface module. |
| A2030 RESOLVER AUTOTUNE ERR | Cause: Resolver autotuning routines, which are automatically started when resolver input is activated for the first time, have failed. Solution: 1. Check cable between resolver and resolver interface module (FEN-21) and order of connector signal wires at both ends of cable. 2. Check resolver parameter settings. For resolver parameters and information, see parameter group 92 Resolver conf. Note: Resolver autotuning routines should always be performed after resolver cable connection has been modified. Autotuning routines can be activated by setting parameter 92.02 Exc signal ampl or 92.03 Exc signal freq, and then setting parameter 90.10 Enc par refresh to Configure. |
| A2031 ENCODER 1 CABLE | Cause: Encoder 1 cable fault detected. Solution: 1. Check cable between FEN-xx interface and encoder 1. After any modifications in cabling, re-configure interface by switching drive power off and on, or by activating parameter 90.10 Enc par refresh. |
| A2032 ENCODER 2 CABLE | Cause: Encoder 2 cable fault detected. Solution: 1. Check cable between FEN-xx interface and encoder 2. After any modifications in cabling, re-configure interface by switching drive power off and on, or by activating parameter 90.10 Enc par refresh. |
| A2033 D2D COMMUNICATION | Cause: On the master drive: The drive has not been replied to by an activated follower for five consecutive polling cycles. On a follower drive: The drive has not received new reference 1 and/or 2 for five consecutive reference handling cycles. Solution: 1. Check that all drives that are polled (parameters 57.04 Follower mask 1 and 57.05 Follower mask 2) on the drive-to- drive link are powered, properly connected to the link, and have the correct node address. 2. Check the drive-to-drive link wiring. 3. Check the settings of parameters 57.06 Ref 1 src and 57.07 Ref 2 src) on the master drive. 4. Check the drive-to-drive link wiring. 5. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 57.02 Comm loss function. |
| A2034 D2D BUFFER OVERLOAD | Cause: Transmission of drive-to-drive references failed because of message buffer overflow. Solution: 1. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 57.02 Comm loss function. |
| A2035 PS COMM | Cause: Communication errors detected between the JCU Control Unit and the power unit of the drive. Solution: 1. Check the connections between the JCU Control Unit and the power unit. |
| A2036 RESTORE | Cause: Restoration of backed-up parameters failed. |
| A2037 CUR MEAS CALIBRATION | Cause: Current measurement calibration will occur at next start. Solution: This is a informative alarm. |
| A2038 AUTOPHASING | Cause: Autophasing will occur at next start. Solution:This is a informative alarm. |
| A2039 EARTH FAULT | Cause: Drive has detected load unbalance typically due to earth fault in motor or motor cable. Solution: 1. Check there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. 2. Check for an earth fault in motor or motor cables by measuring the insulation resistances of motor and motor cable. |
| A2040 AUTORESET | Cause: A fault is to be autoreset. Solution: 1. This is a informative alarm. 2. See parameter group 32 Automatic reset. |
| A2041 MOTOR NOM VALUE | Cause: The motor configuration parameters are set incorrectly or the drive is not dimensioned correctly. Solution: 1. Check the settings of the motor configuration parameters in group 99. 2. Check that the drive is sized correctly for the motor. |
| A2042 D2D CONFIG | Cause: The settings of drive-to-drive link configuration parameters (group 57) are incompatible. Solution: 1. Check the settings of the parameters in group 57 D2D communication. |
| A2043 STALL | Cause: Motor is operating in stall region because of e.g. excessive load or insufficient motor power. Solution: 1. Check motor load and drive ratings. 2. Check fault function parameters. 3. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 30.09 Stall function. |
| A2044 LCURVE | Cause: Overload or underload limit has been exceeded. Solution: 1. Check the settings of the parameters in group 34 User load curve. 2. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 34.01 Overload func / 34.02 Underload function. |
| A2045 LCURVE PAR | Cause: The load curve has been incorrectly or inconsistently defined. Solution: 1. Check the settings of the parameters in group 34 User load curve. |
| A2046 FLUX REF PAR | Cause: The U/f (voltage/frequency) curve has been incorrectly or inconsistently defined. Solution: 1. Check the settings of the parameters in group 38 Flux ref. |
| A2047 SPEED FEEDBACK | Cause: No speed feedback is received. Solution: 1. Check the settings of the parameters in group 19 Speed calculation. 2. Check encoder installation. See the description of fault 0039 for more information. |
| A2048 OPTION COMM LOSS | Cause: Communication between drive and option module (FEN-xx and/or FIO-xx) is lost. Solution: 1. Check that option modules are properly connected to Slot 1 and (or) Slot 2. 2. Check that option modules or Slot 1/2 connectors are not damaged. To determine whether module or connector is damaged: Test each module individually in Slot 1 and Slot 2. |
| A2049 MOTTEMPAL2 | Cause 1. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 31.05 Mot temp2 prot Estimated motor temperature (based on motor thermal model) has exceeded alarm limit defined by parameter 31.07 Mot temp2 almLim. Solution: 1. Check motor ratings and load. 2. Let motor cool down. 3. Ensure proper motor cooling: Check cooling fan, clean cooling surfaces, etc. 4. Check value of alarm limit. 5. Check motor thermal model settings (parameters 31.09…31.14). Cause 2. Measured motor temperature has exceeded alarm limit defined by parameter 31.07 Mot temp2 almLim. Solution: 1. Check that actual number of sensors corresponds to value set by parameter 31.06 Mot temp2 src. 2. Check motor ratings and load. 3. Let motor cool down. 4. Ensure proper motor cooling: Check cooling fan, clean cooling surfaces, etc. 5. Check value of alarm limit. |
| A2050 IGBTOLALARM | Cause: Excessive IGBT junction to case temperature. This fault protects the IGBT(s) and can be activated by a short circuit in the motor cable. Solution: 1. Check motor cable. |
| A2051 IGBTTEMPALARM | Cause: Drive IGBT temperature is excessive. Fault trip limit is 100%. Solution: 1. Check ambient conditions. 2. Check air flow and fan operation. 3. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 4. Check motor power against drive power. |
| A2052 COOLALARM | Cause: Drive module temperature is excessive. Solution: 1. Check ambient temperature. If it exceeds 40 °C (104 °F), ensure that load current does not exceed derated load capacity of drive. See appropriate Hardware Manual. 2. Check drive module cooling air flow and fan operation. 3. Check inside of cabinet and heatsink of drive module for dust pick-up. Clean whenever necessary. |
| A2053 MENU CHG PASSWORD REQ | Cause: Loading a parameter listing requires a password. Solution: Enter password at parameter 16.03 Pass code. |
| A2054 MENU CHANGED | Cause: A different parameter listing is being loaded. Solution: This is a informative alarm. |
| A2055 DEVICE CLEAN | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2056 COOLING FAN | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2057 ADD COOLING | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2058 CABINET FAN | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2059 DC CAPACITOR | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2060 MOTOR BEARING | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2061 MAIN CONTACTOR | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2062 RELAY OUTPUT SW | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2063 MOTOR START COUNT | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2064 POWER UP COUNT | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2065 DC CHARGE COUNT | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2066 ONTIME1 ALARM | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2067 ONTIME2 ALARM | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2068 EDGE1 ALARM | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2069 EDGE2 ALARM | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2070 VALUE1 ALARM | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2071 VALUE2 ALARM | Cause: Maintenance alarm. Solution: See parameter group 44 Maintenance. |
| A2400 SOLUTION ALARM | Cause: Alarm generated by custom application program. Solution: 1. Check custom application program. |
| F0001 OVERCURRENT | Cause: Output current has exceeded internal fault limit. Solution: 1. Check motor load. 2. Check acceleration times in parameter group 22 Speed ref ramp. 3. Check motor and motor cable (including phasing and delta/star connection). 4. Check that the start-up data in parameter group 99 corresponds to the motor rating plate. 5. Check that there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. 6. Check encoder cable (including phasing). |
| F0002 DC OVERVOLTAGE | Cause: Excessive intermediate circuit DC voltage Solution: 1. Check that overvoltage controller is on, parameter 47.01 Overvolt ctrl. 2. Check mains for static or transient overvoltage. 3. Check brake chopper and resistor (if used). 4. Check deceleration time. 5. Use coast-to-stop function (if applicable). 6. Retrofit frequency converter with brake chopper and brake resistor. |
| F0003 DEVICE OVERTEMP | Cause: Measured drive temperature has exceeded internal fault limit. Solution: 1. Check ambient conditions. 2. Check air flow and fan operation. 3. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 4. Check motor power against unit power. |
| F0004 SHORT CIRCUIT | Cause: Short-circuit in motor cable(s) or motor Solution: 1. Check motor and motor cable. 2. Check there are no power factor correction 3. capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. |
| F0005 DC UNDERVOLTAGE | Cause: Intermediate circuit DC voltage is not sufficient due to missing mains phase, blown fuse or rectifier bridge internal fault. Solution: 1. Check mains supply and fuses. |
| F0006 EARTH FAULT | Cause: Drive has detected load unbalance typically due to earth fault in motor or motor cable. Solution: 1. Check there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. 2. Check that there is no earth fault in motor or motor cables: – measure insulation resistances of motor and motor cable. |
| F0007 FAN FAULT | Cause: Fan is not able to rotate freely or fan is disconnected. Fan operation is monitored by measuring fan current. Solution: 1. Check fan operation and connection. |
| F0008 IGBT OVERTEMP | Cause: Drive temperature based on thermal model has exceeded internal fault limit. Solution: 1. Check ambient conditions. 2. Check air flow and fan operation. 3. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 4. Check motor power against unit power. |
| F0009 BC WIRING | Cause: Brake resistor short circuit or brake chopper control fault Solution: 1. Check brake chopper and brake resistor connection. 2. Ensure brake resistor is not damaged. |
| F0010 BC SHORT CIRCUIT | Cause: Short circuit in brake chopper IGBT Solution: 1. Replace brake chopper. 2. Ensure brake resistor is connected and not damaged. |
| F0011 BC OVERHEAT | Cause: Brake chopper IGBT temperature has exceeded internal alarm limit. Solution: 1. Let chopper cool down. 2. Check resistor overload protection function settings (parameters 48.01…48.05). 3. Check that braking cycle meets allowed limits. 4. Check that drive supply AC voltage is not excessive. |
| F0012 BR OVERHEAT | Cause: Brake resistor temperature has exceeded fault limit defined by parameter 48.06 Br temp faultlimit. Solution: 1. Stop drive. 2. Let resistor cool down. 3. Check resistor overload protection function settings (parameters 48.01…48.05). 4. Check fault limit setting, parameter 48.06 Br temp faultlim. 5. Check that braking cycle meets allowed limits. |
| F0013 CURR MEAS GAIN | Cause: Difference between output phase U2 and W2 current measurement gain is too great. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0014 CABLE CROSS CONNECTION | Cause: Incorrect input power and motor cable connection (i.e. input power cable is connected to drive motor connection). Solution: 1. Check input power connections. |
| F0015 SUPPLY PHASE | Cause: Intermediate circuit DC voltage is oscillating due to missing input power line phase or blown fuse. Solution: 1. Check input power line fuses. 2. Check for input power supply imbalance. |
| F0016 MOTOR PHASE | Cause: Motor circuit fault due to missing motor connection (all three phases are not connected). Solution: 1. Connect motor cable. |
| F0017 ID-RUN FAULT | Cause: Motor ID Run is not completed successfully. Solution: 1. Check motor settings (parameters 99.04…99.13). 2. Check that no limits prevent ID run. The following must apply: 20.05 Maximum current > 99.06 Mot nom current 3. For Reduced and Normal ID run: – 20.01 Maximum speed > 55% of 99.09 Mot nom speed – 20.02 Minimum speed < 0 – Supply voltage > 65% of 99.07 Mot nom voltage – Maximum torque (selected by 20.06 Torq lim sel) > 100% (only for Normal ID run). 4. Retry. |
| F0018 CURR U2 MEAS | Cause: Measured offset error of U2 output phase current measurement is too great. (Offset value is updated during current calibration.) Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0019 CURR V2 MEAS | Cause: Measured offset error of V2 output phase current measurement is too great. (Offset value is updated during current calibration.) Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0020 CURR W2 MEAS | Cause: Measured offset error of W2 output phase current measurement is too great. (Offset value is updated during current calibration.) Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0021 STO1 LOST | Cause: Safe Torque Off function is active, i.e. safety circuit signal 1 connected between X6:1 and X6:3 is lost while drive is at stopped state and parameter 30.07 Sto diagnostic is set to Alarm or No. Solution: 1. Check safety circuit connections. |
| F0022 STO2 LOST | Cause: Safe Torque Off function is active, i.e. safety circuit signal 2 connected between X6:2 and X6:4 is lost while drive is at stopped state and parameter 30.07 Sto diagnostic is set to Alarm or No. Solution: 1. Check safety circuit connections. |
| F0023 STO MODE CHANGE | Cause: Error in changing Safe Torque Off supervision, i.e. parameter 30.07 Sto diagnostic setting could not be changed to value Fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0024 INTBOARD OVERTEMP | Cause: Interface board (between power unit and control unit) temperature has exceeded internal fault limit. Solution: 1. Let drive cool down. |
| F0025 BC MOD OVERTEMP | Cause: Input bridge or brake chopper temperature has exceeded internal fault limit. Solution: 1. Let drive cool down. |
| F0026 AUTOPHASING | Cause: Autophasing routine failed. Solution: Try other autophasing modes (see parameter 11.07 Autophasing mode) if possible. |
| F0027 PU LOST | Cause: Connection between the JCU Control Unit and the power unit of the drive is lost. Solution: 1. Check the connections between the JCU 2. Control Unit and the power unit. |
| F0028 PS COMM | Cause: Communication errors detected between the JCU Control Unit and the power unit of the drive. Solution: 1. Check the connections between the JCU Control Unit and the power unit. |
| F0029 IN CHOKE TEMP | Cause: Temperature of internal AC choke excessive. Solution: 1. Check cooling fan. |
| F0030 EXTERNAL | Cause: Fault in external device. (This information is configured through one of programmable digital inputs.) Solution: 1. Check external devices for faults. 2. Check parameter 30.01 External fault setting. |
| F0031 SAFE TORQUE OFF | Cause: Safe Torque Off function is active, i.e. safety circuit signal(s) connected to connector X6 is lost during start or run, or while drive is stopped and parameter 30.07 Sto diagnostic is set to Fault. Solution: 1. Check safety circuit connections. |
| F0032 OVERSPEED | Cause: Motor is turning faster than highest allowed speed due to incorrectly set minimum/ maximum speed, insufficient braking torque or changes in load when using torque reference. Solution: 1. Check minimum/maximum speed settings, parameters 20.01 Maximum speed and 20.02 Minimum speed. 2. Check adequacy of motor braking torque. 3. Check applicability of torque control. 4. Check need for brake chopper and resistor(s). |
| F0033 BRAKE START TORQUE | Cause: Mechanical brake fault. Fault is activated if required motor starting torque (42.08 Brake open torq) is not achieved. Solution: 1. Check brake open torque setting, parameter 42.08. 2. Check drive torque and current limits. 3. See parameter group 20 Limits. |
| F0034 BRAKE NOT CLOSED | Cause: Mechanical brake control alarm. Fault is activated e.g. if brake acknowledgement is not as expected during brake closing. Solution: 1. Check mechanical brake connection. 2. Check mechanical brake settings in parameter group 42 Mech brake ctrl. 3. To determine whether problem is with acknowledgement signal or brake, check if brake is closed or open. |
| F0035 BRAKE NOT OPEN | Cause: Mechanical brake control alarm. Fault is activated e.g. if brake acknowledgement is not as expected during brake opening. Solution: 1. Check mechanical brake connection. 2. Check mechanical brake settings in parameter group 42 Mech brake ctrl. 3. To determine whether problem is with acknowledgement signal or brake, check if brake is closed or open. |
| F0036 LOCAL CTRL LOSS | Cause: Control panel or PC tool selected as active control location for drive has ceased communicating. Solution: 1. Check PC tool or control panel connection. 2. Check control panel connector. 3. Replace control panel in mounting platform. |
| F0037 NVMEM CORRUPTED | Cause: Drive internal fault. Note: This fault cannot be reset. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0038 OPTION COMM LOSS | Cause: Communication between drive and option module (FEN-xx and/or FIO-xx) is lost. Solution: 1. Check that option modules are properly connected to Slot 1 and (or) Slot 2. 2. Check that option modules or Slot 1/2 connectors are not damaged. To determine whether module or connector is damaged: Test each module individually in Slot 1 and Slot 2. |
| F0039 ENCODER1 | Cause: Encoder 1 feedback fault. Solution: 1. If fault appears during first start-up before encoder feedback is used: – Check cable between encoder and encoder interface module (FEN-xx) and order of connector signal wires at both ends of cable. 2. If fault appears after encoder feedback has already been used or during drive run: – Check that encoder connection wiring or encoder is not damaged. – Check that encoder interface module (FEN-xx) connection or module is not damaged. – Check earthings (when disturbances are detected in communication between encoder interface module and encoder). |
| F0040 ENCODER2 | Cause: Encoder 2 feedback fault. Solution: 1. If fault appears during first start-up before encoder feedback is used: – Check cable between encoder and encoder interface module (FEN-xx) and order of connector signal wires at both ends of cable. 2. If fault appears after encoder feedback has already been used or during drive run: – Check that encoder connection wiring or encoder is not damaged. – Check that encoder interface module (FEN-xx) connection or module is not damaged. – Check earthings (when disturbances are detected in communication between encoder interface module and encoder). |
| F0045 FIELDBUS COMM | Cause: Cyclical communication between drive and fieldbus adapter module or between PLC and fieldbus adapter module is lost. Solution: 1. Check status of fieldbus communication. 2. Check settings of parameter group 50 Fieldbus. 3. Check cable connections. 4. Check if communication master is able to communicate. |
| F0046 FB MAPPING FILE | Cause: Drive internal fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0047 MOTOR OVERTEMP | Cause 1: Estimated motor temperature (based on motor thermal model) has exceeded fault limit defined by parameter 31.04 Mot temp1 fltLimit. Solution: 1. Check motor ratings and load. 2. Let motor cool down. Ensure proper motor cooling: Check cooling fan, 3. clean cooling surfaces, etc. 4. Check value of alarm limit. 5. Check motor thermal model settings (parameters 31.09…31.14). Cause 2: Measured motor temperature has exceeded fault limit defined by parameter 31.04 Mot temp1 fltLim. Solution: 1. Check that actual number of sensors corresponds to value set by parameter 31.02 Mot temp1 src. 2. Check motor ratings and load. 3. Let motor cool down. 4. Ensure proper motor cooling: Check cooling fan, clean cooling surfaces, etc. 5. Check value of alarm limit. |
| F0049 AI SUPERVISION | Cause: An analogue input has reached limit defined by parameter 13.33 AI superv cw. Solution: 1. Check analogue input source and connections. 2. Check analogue input minimum and maximum limit settings. |
| F0050 ENCODER 1 CABLE | Cause: Encoder 1 cable fault detected. Solution: 1. Check cable between FEN-xx interface and encoder 1. 2. After any modifications in cabling, re-configure interface by switching drive power off and on, or by activating parameter 90.10 Enc par refresh. |
| F0051 ENCODER 2 CABLE | Cause: Encoder 2 cable fault detected. Solution: 1. Check cable between FEN-xx interface and encoder 2. 2. After any modifications in cabling, re-configure interface by switching drive power off and on, or by activating parameter 90.10 Enc par refresh. |
| F0052 D2D CONFIG | Cause: Configuration of the drive-to- drive link has failed for a reason other than those indicated by alarm A-2042, for example start inhibition is requested but not granted. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0053 D2D COMM | Cause 1: On the master drive: The drive has not been replied to by an activated follower for five consecutive polling cycles. Solution: 1. Check that all drives that are polled (parameters 57.04 Follower mask 1 and 57.05 Follower mask 2) on the drive-to- drive link are powered, properly connected to the link, and have the correct node address. 2. Check the drive-to-drive link wiring. Cause 2: On a follower drive: The drive has not received new reference 1 and/or 2 for five consecutive reference handling cycles. Solution: 1. Check the settings of parameters 57.06 Ref 1 src and 57.07 Ref 2 src) on the master drive. 2. Check the drive-to-drive link wiring. |
| F0054 D2D BUF OVERLOAD | Cause: Transmission of drive-to-drive references failed because of message buffer overflow. Solution: 1. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 90.05 Enc cable fault. 2. There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0055 TECH LIB | Cause: Resettable fault generated by a technology library. Solution: Refer to the documentation of the technology library. |
| F0056 TECH LIB CRITICAL | Cause: Permanent fault generated by a technology library. Solution: Refer to the documentation of the technology library. |
| F0057 FORCED TRIP | Cause: Generic Drive Communication Profile trip command. Solution: Check PLC status. |
| F0058 FB PAR ERROR | Cause: The drive does not have a functionality requested by PLC, or requested functionality has not been activated. Solution: 1. Check PLC programming. 2. Check settings of parameter group 50 Fieldbus. |
| F0059 STALL | Cause: Motor is operating in stall region because of e.g. excessive load or insufficient motor power. Solution: 1. Check motor load and drive ratings. 2. Check fault function parameters. 3. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 30.09 Stall function. |
| F0060 LOAD CURVE | Cause: Overload or underload limit has been exceeded. Solution: 1. Check the settings of the parameters in group 34 User load curve. |
| F0061 SPEED FEEDBACK | Cause: No speed feedback is received. Solution: 1. Check the settings of the parameters in group 19 Speed calculation. 2. Check encoder installation. See the description of fault 0039 (ENCODER1) for more information. |
| F0062 D2D SLOT COMM | Cause: Drive-to-drive link is set to use an FMBA module for communication, but no module is detected in specified slot. Solution: 1. Check the settings of parameters 57.01 and 57.15. Ensure that the FMBA module has been detected by checking parameters 09.20…09.22. 2. Check that the FMBA module is correctly wired. 3. Try installing the FMBA module into another slot. |
| F0063 MOTOR TEMP2 | Cause 1: Estimated motor temperature (based on motor thermal model) has exceeded fault limit defined by parameter 31.08 Mot temp2 fltLim. Solution: 1. Check motor ratings and load. 2. Let motor cool down. 3. Ensure proper motor cooling: Check cooling fan, clean cooling surfaces, etc. 4. Check value of alarm limit. 5. Check motor thermal model settings (parameters 31.09…31.14). Cause 2: Measured motor temperature has exceeded fault limit defined by parameter 31.08 Mot temp2 fltLim. Solution: 1. Check that actual number of sensors corresponds to value set by parameter 31.06 Mot temp2 src. 2. Check motor ratings and load. 3. Let motor cool down. 4. Ensure proper motor cooling: Check cooling fan, clean cooling surfaces, etc. 5. Check value of alarm limit. |
| F0064 IGBT OVERLOAD | Cause: Excessive IGBT junction to case temperature. This fault protects the IGBT(s) and can be activated by a short circuit in the motor cable. Solution: 1. Check motor cable. |
| F0065 IGBT TEMP | Cause: Drive IGBT temperature is excessive. Fault trip limit is 100%. Solution: 1. Check ambient conditions. 2. Check air flow and fan operation. 3. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 4. Check motor power against drive power. |
F0066 COOLING | Cause: Drive module temperature is excessive. Solution: 1. Check ambient temperature. If it exceeds 40 °C (104 °F), ensure that load current does not exceed derated load capacity of drive. See appropriate Hardware Manual. 2. Check drive module cooling air flow and fan operation. 3. Check inside of cabinet and heatsink of drive module for dust pick-up. Clean whenever necessary. |
| F0201 T2 OVERLOAD | Cause: Firmware time level 2 overload. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0202 T3 OVERLOAD | Cause: Firmware time level 3 overload. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0203 T4 OVERLOAD | Cause: Firmware time level 4 overload. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0204 T5 OVERLOAD | Cause: Firmware time level 5 overload. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0205 A1 OVERLOAD | Cause: Application time level 1 fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0206 A2 OVERLOAD | Cause: Application time level 2 fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0207 A1 INIT FAULT | Cause: Application task creation fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0208 A2 INIT FAULT | Cause: Application task creation fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0209 STACK ERROR | Cause: Drive internal fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0210 FPGA ERROR | Cause: Drive internal fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0301 UFF FILE READ | Cause: File read error. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0302 APPL DIR CREATION | Cause: Drive internal fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0303 FPGA CONFIG DIR | Cause: Drive internal fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0304 PU RATING ID | Cause: Drive internal fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0305 RATING DATABASE | Cause: Drive internal fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0306 LICENSING | Cause: Drive internal fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0307 DEFAULT FILE | Cause: Drive internal fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0308 APPLFILE PAR | Cause: Corrupted application file. Note: This fault cannot be reset. Solution: 1. Reload application. 2. If fault is still active there is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0309 APPL LOADING | Cause: Corrupted application file. Solution: 1. Reload application. 2. If fault is still active there is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0310 USERSET LOAD | Cause: Loading of user set is not successfully completed because: – requested user set does not exist – user set is not compatible with drive program – drive has been switched off during loading. Solution: 1. Reload. |
| F0311 USERSET SAVE | Cause: User set is not saved because of memory corruption. Solution: 1. Check the setting of parameter 95.01 Ctrl boardSupply. 2. If the fault still occurs there is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0312 UFF OVERSIZE | Cause: UFF file is too big. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0313 UFF EOF | Cause: UFF file structure failure. Solution: 1. Delete file. 2. After this problem remain same then there is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0314 TECH LIB INTERFACE | Cause: Incompatible firmware interface. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0315 RESTORE FILE | Cause: Restoration of backed-up parameters failed. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0316 DAPS MISMATCH | Cause: Mismatch between JCU Control Unit firmware and power unit logic versions. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |
| F0317 SOLUTION FAULT | Cause: Fault generated by function block SOLUTION_FAULT in the solution program. Solution: 1. Check the usage of the SOLUTION_FAULT block in the solution program. |
| F0318 MENU HIDING | Cause: Menu hiding file missing or corrupted. Solution: Reload application. |
| A2076 TEMP MEAS FAILURE | Cause: Problem with internal temperature measurement of the drive. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive, need to repaur or replace drive. |