
Download Links
 Download Catalog Download Catalog |
 Download Manual Download Manual |
 Download Crane Manual Download Crane Manual |
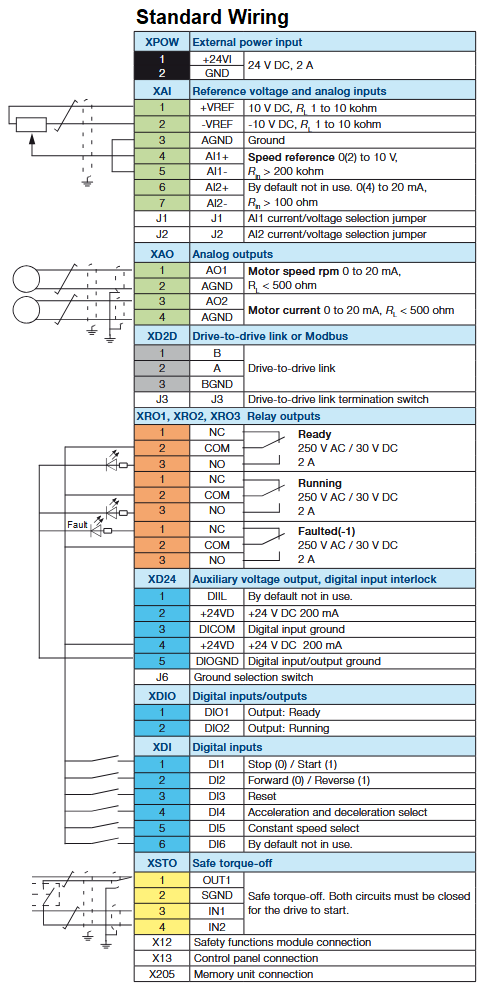
Wiring Details
Below image show terminal details:
Brake Resistance Details
| Model no. | R. Min | P.BR Max |
| 3-phase, 380 to 480 V | ohm | KW |
| ACS880-01-02A4-3 | 78 | 0.75 |
| ACS880-01-03A3-3 | 78 | 1.1 |
| ACS880-01-04A0-3 | 78 | 1.5 |
| ACS880-01-05A6-3 | 78 | 2.2 |
| ACS880-01-07A2-3 | 78 | 3 |
| ACS880-01-09A4-3 | 78 | 4 |
| ACS880-01-12A6-3 | 78 | 5.5 |
| ACS880-01-017A-3 | 39 | 7.5 |
| ACS880-01-025A-3 | 39 | 11 |
| ACS880-01-032A-3 | 19 | 15 |
| ACS880-01-038A-3 | 19 | 18.5 |
| ACS880-01-045A-3 | 13 | 22 |
| ACS880-01-061A-3 | 13 | 22 |
Faults & Alarms
Search from below list for ACS880 drive faults & alarms:
| Fault Code | Cause & Solution |
|---|---|
| A2A1 Current calibration | Cause: Current offset and gain measurement calibration will occur at next start. Solution: This is an Informative warning. (See parameter 99.13 ID run requested.) |
| A2B1 Overcurrent | Cause: Output current has exceeded internal fault limit. In addition to an actual overcurrent situation, this warning may also be caused by an earth fault or supply phase loss. Solution: 1. Check motor load. 2. Check acceleration times in parameter group 23 Speed reference ramp (speed control), 26 Torque reference chain (torque control) or 28 Frequency reference chain (frequency control). 3. Also check parameters 46.01 Speed scaling, 46.02 Frequency scaling and 46.03 Torque scaling. 4.Check motor and motor cable (including phasing and delta/star connection). 5. Check for an earth fault in motor or motor cables by measuring the insulation resistances of motor and motor cable. See chapter Electrical installation, section 6. Checking the insulation of the assembly in the hardware manual of the drive. 7. Check there are no contactors opening and closing in motor cable. 8. Check that the start-up data in parameter group 99 Motor data corresponds to the motor rating plate. 9. Check that there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. |
| A2B3 Earth leakage | Cause: Drive has detected load unbalance typically due to earth fault in motor or motor cable. Solution 1. Check there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. 2. Check for an earth fault in motor or motor cables by measuring the insulation resistances of motor and motor cable. 3. Check the insulation of the assembly in the hardware manual of the drive. If an earth fault is found, fix or change the motor cable and/or motor. 4. If no earth fault can be detected then hardware issue in drive. |
| A2B4 Short circuit | Cause: Short-circuit in motor cable(s) or motor. Solution: 1. Check motor and motor cable for cabling errors. 2. Check motor and motor cable (including phasing and delta/star connection). 3. Check for an earth fault in motor or motor cables by measuring the insulation resistances of motor and motor cable. 4. Check there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. |
| A2BA IGBT overload | Cause: Excessive IGBT junction to case temperature. This warning protects the IGBT(s) and can be activated by a short circuit in the motor cable. Solution: 1. Check motor cable. 2. Check ambient conditions. 3. Check air flow and fan operation. 4. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 5. Check motor power against drive power. |
| A3A1 DC link overvoltage | Cause: Intermediate circuit DC voltage too high (when the drive is stopped). Solution: 1. Check the supply voltage setting (parameter 95.01 Supply voltage). Note that the wrong setting of the parameter may cause the motor to rush uncontrollably, or may overload the brake chopper or resistor. 2. Check the supply voltage. 3. If the problem persists, then hardware issue in drive or other issue in drive. |
| A3A2 DC link undervoltage | Cause: Intermediate circuit DC voltage too low (when the drive is stopped). Solution: 1. Check the supply voltage setting (parameter 95.01 Supply voltage). Note that the wrong setting of the parameter may cause the motor to rush uncontrollably, or may overload the brake chopper or resistor. 2. Check the supply voltage. 3. If the problem persists, then hardware issue in drive or other issue in drive. |
| A3AA DC not charged | Cause: The voltage of the intermediate DC circuit has not yet risen to operating level. Solution: 1. Check the supply voltage setting (parameter 95.01 Supply voltage). Note that the wrong setting of the parameter may cause the motor to rush uncontrollably, or may overload the brake chopper or resistor. 2. Check the supply voltage. 3. If the problem persists, then hardware issue in drive or other issue in drive. |
| A3C1 DC voltage difference | Cause: Difference in DC voltages between parallel-connected inverter modules. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| A490 Incorrect temperature sensor setup | Cause: Sensor type mismatch. Solution: Check the settings of temperature source parameters 35.11. |
| A491 External temperature 1 | Cause: Measured temperature 1 has exceeded warning limit. Solution 1. Check the value of parameter 35.02 Measured temperature 1. 2. Check the cooling of the motor (or other equipment whose temperature is being measured). 3. Check the value of 35.13 Temperature 1 warning limit. |
| A4A1 IGBT overtemperature | Cause: Estimated drive IGBT temperature is excessive. Solution: 1. Check ambient conditions. 2. Check air flow and fan operation. 3. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 4. Check motor power against drive power. |
| A4A9 Cooling | Cause: Drive module temperature is excessive. Solution: 1. Check ambient temperature. If it exceeds 50 °C /122 °F, ensure that load current does not exceed derated load capacity of drive. 2. Check drive module cooling air flow and fan operation. 3. Check inside of cabinet and heatsink of drive module for dust pick-up. Clean whenever necessary. |
| A4B0 Excess temperature | Cause: Power unit module temperature is excessive. Solution: Check ambient conditions. Check air flow and fan operation. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. Check motor power against drive power. |
| A4B1 Excess temperature difference | Cause: High temperature difference between the IGBTs of different phases. Solution: 1. Check the motor cabling. 2. Check cooling of drive module(s). |
| A4F6 IGBT temperature | Cause: Drive IGBT temperature is excessive. Solution: Check ambient conditions. Check air flow and fan operation. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. Check motor power against drive power. |
| A580 PU communication | Cause: Communication errors detected between the drive control unit and the power unit. Solution: 1. Check the connections between the drive control unit and the power unit. |
| A5A0 Safe torque off | Cause: Safe torque off function is active, ie safety circuit signal(s) connected to connector STO is lost. Solution: 1. Check safety circuit connections. 2. Check parameter 31.22 STO indication run/stop. |
| A5EA Measurement circuit temperature | Cause: Problem with internal temperature measurement of the drive. Solution: 1. Check drive hardware. 2. May be hardware issue in drive. |
| A5EB PU board powerfail | Cause: Power unit power supply failure. Solution: 1. Check drive hardware. 2. May be hardware issue in drive. |
| A5EC PU communication internal | Cause: Communication errors detected between the drive control unit and the power unit. Solution: 1. Check the connections between the drive control unit and the power unit. |
| A5ED Measurement circuit ADC | Cause: Measurement circuit fault. Solution: 1. Check drive hardware. 2. May be hardware issue in drive. |
| A5EE Measurement circuit DFF | Cause: Measurement circuit fault. Solution: 1. Check drive hardware. 2. May be hardware issue in drive. |
| A5EF PU state feedback | Cause: State feedback from output phases does not match control signals. Solution: 1. Check drive hardware. 2. May be hardware issue in drive. |
| A5F0 Charging feedback | Cause: Charging feedback signal missing. Solution: 1. Check the feedback signal coming from the charging system. |
| A6A4 Motor nominal value | Cause: The motor parameters are set incorrectly. The drive is not dimensioned correctly. Solution: 1. Check the settings of the motor configuration parameters in group 99. 2. Check that the drive is sized correctly for the motor. |
| A6A5 No motor data | Cause: Parameters in group 99 have not been set. Solution: 1. Check that all the required parameters in group 99 have been set. Note: It is normal for this warning to appear during the start-up and continue until the motor data is entered. |
| A6A6 Voltage category unselected | Cause: The voltage category has not been defined. Solution: Set voltage category in parameter 95.01 Supply voltage. |
| A6D1 FBA A parameter conflict | Cause: The drive does not have a functionality requested by a PLC, or requested functionality has not been activated. Solution: 1. Check PLC programming. 2. Check settings of parameter groups 50 Fieldbus adapter (FBA). |
| A6E5 AI parametrization | Cause: The current/voltage hardware setting of an analog input does not correspond to parameter settings. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. The code identifies the analog input whose settings are in conflict. Adjust parameter 12.15/ 12.25. Note: Control board reboot (either by cycling the power or through parameter 96.08 Control board boot) is required to validate any changes in the hardware settings. |
| A780 Motor stall | Cause: Motor is operating in stall region because of e.g. excessive load or insufficient motor power. Solution: 1. Check motor load and drive ratings. 2. Check fault function parameters. 3. This is a programmable warning check parameter 31.24 Stall function. |
| A782 FEN temperature | Cause 1: Error in temperature measurement when temperature sensor (KTY or PTC) connected to encoder interface FEN-xx is used. Solution: Check that parameter 35.11 Supervision 1 source / 35.21 Supervision 2 source setting corresponds to actual encoder interface installation. Cause 2: Error in temperature measurement when KTY sensor connected to encoder interface FEN-01 is used. Solution: FEN-01 does not support temperature measurement with KTY sensor. Use PTC sensor or other encoder interface module. |
| A791 Brake resistor | Cause: Brake resistor broken or not connected. Solution: 1. Check that a brake resistor has been connected. 2. Check the condition of the brake resistor. |
| A793 BR excess temperature | Cause: Brake resistor temperature has exceeded warning limit defined by parameter 43.12 Brake resistor warning limit. Solution: 1. Stop drive. Let resistor cool down. 2. Check resistor overload protection function settings (parameter group 43 Brake chopper). 3. Check warning limit setting, parameter 43.12 Brake resistor warning limit. 4. Check that the resistor has been dimensioned correctly. 5. Check that braking cycle meets allowed limits. |
| A794 Brake resistor wiring | Cause: Brake resistor short circuit or brake chopper control fault Solution: 1. Check brake chopper and brake resistor connection. 2. Ensure brake resistor is not damaged. |
| A79B BC short circuit | Cause: Short circuit in brake chopper IGBT. Solution: – Replace brake chopper (if external). – Drives with internal choppers will need to be returned to ABB. – Ensure connection and no damages to brake resistor. |
| A79C BC IGBT excess temperature | Cause: Brake chopper IGBT temperature has exceeded internal warning limit. Solution: 1. Let chopper cool down. 2. Check for excessive ambient temperature. 3. Check for cooling fan failure. 4. Check for obstructions in the air flow. 5 Check the dimensioning and cooling of the cabinet. 6. Check resistor overload protection function settings (parameters 43.06… 43.10). 7. Check minimum allowed resistor value for the chopper being used. 9. Check that braking cycle meets allowed limits. 10 Check that drive supply AC voltage is not excessive. |
| A7A1 Mechanical brake closing failed | Cause: Mechanical brake control warning. Solution: 1. Check mechanical brake connection. 2. Check mechanical brake settings in parameter group 44 Mechanical brake control. 3. Check that acknowledgment signal matches the actual status of the brake. |
| A7A2 Mechanical brake opening failed | Cause: Status of mechanical brake acknowledgment is not as expected during brake open. Solution: 1. Check mechanical brake connection. 2. Check mechanical brake settings in parameter group 44 Mechanical brake control. 3. Check that acknowledgment signal matches the actual status of brake. |
| A7A5 Mechanical brake opening not allowed | Cause: Open conditions of mechanical brake cannot be fulfilled (e.g., brake has been prevented from opening by parameter 44.11) Solution: 1. Check mechanical brake settings in parameter group 44 Mechanical brake control (especially 44.11). 2. Check that the acknowledgment signal (if used) matches the actual status of the brake. |
| A7B0 Motor speed feedback | Cause: Motor speed feedback has failed and drive continues operation with open loop control. Solution: 1. Check the settings of the parameters in groups 90 Feedback selection, 91 Encoder module settings and 92 Encoder 1 configuration. 2. Check encoder installation. 3. This is a Programmable warning: check parameter 90.45 Motor feedback fault. |
| A7C1 FBA A communication | Cause: Cyclical communication between drive and fieldbus adapter module A or between PLC and fieldbus adapter module A is lost. Solution: 1. Check status of fieldbus communication. 2. Check settings of parameter groups 50 Fieldbus adapter (FBA), 51 FBA A settings, 52 FBA A data in and 53 FBA A data out. 3. Check cable connections. 4. Check if communication master is able to communicate. 5. This is a Programmable warning: check parameter 50.02 FBA A comm loss function. |
| A7E1 Encoder 1 | Cause: Encoder 1 error. Solution: 1. Check that the parameter settings in groups 92 Encoder 1 configuration are correct. Note: New settings will only take effect after parameter 91.10 Encoder parameter refresh is used or after the drive control unit is powered up the next time. 2. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. See appropriate actions for each code below. – Aux code: 410 Data read error- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 411 Overspeed- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 412 Pulse overfrequency- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 413 Cable fault Check the wiring of the encoder. See also parameters 92.20 Enc cable fault func and 92.21 Enc cable fault mode. – Aux code: 414 Resolver ID run fault- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 415 Resolver SW version- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 416 Resolver speed scale- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 424 Data read error- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 425 Cable fault mode not supported Current setting of 92.21 Enc cable fault mode not supported by the FEN-xx module. – Aux code: 514 Communication loss Check the wiring of the encoder. |
| A7E2 Encoder 2 | Cause: Encoder 2 has been activated by parameter but the encoder interface (FEN-xx) cannot be found. Solution: 1. Check that the parameter settings in groups 93 Encoder 2 configuration are correct. Note: New settings will only take effect after parameter 91.10 Encoder parameter refresh is used or after the drive control unit is powered up the next time. 2. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. – Aux code: 410 Data read error- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 411 Overspeed- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 412 Pulse overfrequency- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 413 Cable fault Check the wiring of the encoder. See also parameters 92.20 Enc cable fault func and 92.21 Enc cable fault mode. – Aux code: 414 Resolver ID run fault- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 415 Resolver SW version- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 416 Resolver speed scale- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 424 Data read error- There is an hardware or software issue. – Aux code: 425 Cable fault mode not supported Current setting of 92.21 Enc cable fault mode not supported by the FEN-xx module. – Aux code: 514 Communication loss Check the wiring of the encoder. |
| A7EE Panel loss | Cause: Control panel or PC tool selected as active control location for drive has ceased communicating. Solution: 1. Check PC tool or control panel connection. 2. Check control panel connector. 3. Check mounting platform if being used. Disconnect and reconnect the control panel. 4. This is a programmable warning check parameter 49.05 Communication loss action. |
| A880 Motor bearing warning | Cause: Warning generated by an on-time timer or a value counter. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the warning corresponding to the code: – 0: 33.13 On-time 1 source – 1: 33.23 On-time 2 source – 4: 33.53 Value counter 1 source – 5: 33.63 Value counter 2 source. 3. This is a Programmable warnings also check following parameter : – 33.14 On-time 1 warning select – 33.24 On-time 2 warning select – 33.55 Value counter 1 warning select – 33.65 Value counter 2 warning selection |
| A881 Output relay warning | Cause: Warning generated by an edge counter. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the warning corresponding to the code: – 2: 33.33 Edge counter 1 source – 3: 33.43 Edge counter 2 source. 3. This is a Programmable warnings also check following parameters: – 33.35 Edge counter 1 warning selection – 33.45 Edge counter 2 warning selection |
| A882 Motor starts warning | Cause: Warning generated by an edge counter. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the warning corresponding to the code: – 2: 33.33 Edge counter 1 source – 3: 33.43 Edge counter 2 source. 3. This is a Programmable warnings also check following parameters: – 33.35 Edge counter 1 warning selection – 33.45 Edge counter 2 warning selection |
| A883 Power ups warning | Cause: Warning generated by an edge counter. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the warning corresponding to the code: – 2: 33.33 Edge counter 1 source – 3: 33.43 Edge counter 2 source. 3. This is a Programmable warnings also check following parameters: – 33.35 Edge counter 1 warning selection – 33.45 Edge counter 2 warning selection |
| A884 Main contactor warning | Cause: Warning generated by an edge counter. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the warning corresponding to the code: – 2: 33.33 Edge counter 1 source – 3: 33.43 Edge counter 2 source. 3. This is a Programmable warnings also check following parameters: – 33.35 Edge counter 1 warning selection – 33.45 Edge counter 2 warning selection |
| A885 DC charge warning | Cause: Warning generated by an edge counter. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the warning corresponding to the code: – 2: 33.33 Edge counter 1 source – 3: 33.43 Edge counter 2 source. 3. This is a Programmable warnings also check following parameters: – 33.35 Edge counter 1 warning selection – 33.45 Edge counter 2 warning selection |
| A886 On-time 1 warning | Cause: Warning generated by on-time timer 1. Solution: 1. Check the source of the warning (parameter 33.13 On-time 1 source). 2. This is a Programmable warning: check parameter 33.14 On-time 1 warning select. |
| A887 On-time 2 warning | Cause: Warning generated by on-time timer 2. Solution: 1. Check the source of the warning (parameter 33.23 On-time 2 source). 2. This is a Programmable warning: check parameter 33.24 On-time 2 warning select. |
| A888 Edge counter 1 warning | Cause: Warning generated by edge counter 1. Solution: 1. Check the source of the warning (parameter 33.33 Edge counter 1 source). 2. This is a Programmable warning: check parameter 33.35 Edge counter 1 warning selection. |
| A889 Edge counter 2 warning | Cause: Warning generated by edge counter 2. Solution: 1. Check the source of the warning (parameter 33.43 Edge counter 2 source). 2. This is a Programmable warning: check parameter 33.45 Edge counter 2 warning selection. |
| A88A Value integrator 1 warning | Cause: Warning generated by value counter 1. Solution: 1. Check the source of the warning (parameter 33.53 Value counter 1 source). 2. This is a Programmable warning: check parameter 33.55 Value counter 1 warning select. |
| A88B Value integrator 2 warning | Cause: Warning generated by value counter 2. Solution: 1. Check the source of the warning (parameter 33.63 Value counter 2 source). 2. This is a Programmable warning: check parameter 33.65 Value counter 2 warning select. |
| A88C Device clean warning | Cause: Warning generated by an on-time timer. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the warning corresponding to the code: – 0: 33.13 On-time 1 source – 1: 33.23 On-time 2 source – 10: 05.04 Fan on-time counter. 3. This is a Programmable warnings check following parameter also: – 33.14 On-time 1 warning select – 33.24 On-time 2 warning select |
| A88D DC capacitor warning | Cause: Warning generated by an on-time timer. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the warning corresponding to the code: – 0: 33.13 On-time 1 source – 1: 33.23 On-time 2 source – 10: 05.04 Fan on-time counter. 3. This is a Programmable warnings check following parameter also: – 33.14 On-time 1 warning select – 33.24 On-time 2 warning select |
| A88E Cabinet fan warning | Cause: Warning generated by an on-time timer. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the warning corresponding to the code: – 0: 33.13 On-time 1 source – 1: 33.23 On-time 2 source – 10: 05.04 Fan on-time counter. 3. This is a Programmable warnings check following parameter also: – 33.14 On-time 1 warning select – 33.24 On-time 2 warning select |
| A88F Cooling fan warning | Cause: Warning generated by an on-time timer. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the warning corresponding to the code: – 0: 33.13 On-time 1 source – 1: 33.23 On-time 2 source – 10: 05.04 Fan on-time counter. 3. This is a Programmable warnings check following parameter also: – 33.14 On-time 1 warning select – 33.24 On-time 2 warning select |
| A890 Additional cooling fan warning | Cause: Warning generated by an on-time timer. Solution: 1. Check the event log for an auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the warning corresponding to the code: – 0: 33.13 On-time 1 source – 1: 33.23 On-time 2 source – 10: 05.04 Fan on-time counter. 3. This is a Programmable warnings check following parameter also: – 33.14 On-time 1 warning select – 33.24 On-time 2 warning select |
| A8B0 Signal supervision | Cause: Warning generated by a signal supervision function. Solution: 1. Check the source of the warning (parameter 32.07 Supervision 1 signal). 2. This is a programmable warning check parameter 32.06 Supervision 1 action |
A981 External warning 1 | Cause: Fault in external device 1. Soultion: 1. Check the external device. 2. Check setting of parameter 31.01 External event 1 source. 3. This is a Programmable warning: check parameter – 31.01 External event 1 source 31.02 External event 1 type |
| AF8C Process PID sleep mode | Cause: The drive is entering sleep mode. Solution: 1. This is a informative warning. 2. See section Sleep function for process PID control (page 39), and parameters 40.41…40.48. |
AFAA Autoreset | Cause: A fault is about to be autoreset. Solution: 1. This is a informative warning no need to take any action. 2. See the settings in parameter group 31 Fault functions. |
AFE1 Emergency stop (off2) | Cause: Drive has received an emergency stop (mode selection off2) command. Solution: 1. Check that it is safe to continue operation. Then return emergency stop push button to normal position. Restart drive. 2. If the emergency stop was unintentional, check the source selected by parameter 21.05 Emergency stop source. |
AFE2 Emergency stop (off1 or off3) | Cause: Drive has received an emergency stop (mode selection off1 or off3) command. Solution: 1. Check that it is safe to continue operation. Then return emergency stop push button to normal position. Restart drive. 2. If the emergency stop was unintentional, check the source selected by parameter 21.05 Emergency stop source. |
| AFEA Enable start signal missing | Cause: No enable start signal received. Solution: 1. Check the setting of (and the source selected by) parameter 20.19 Enable start command. |
| AFEB Run enable missing | Cause: No run enable signal is received. Solution: 1. Check setting of parameter 20.12 Run enable 1 source. 2. Switch signal on (e.g. in the fieldbus Control Word) or check wiring of selected source. |
| AFF6 Identification run | Cause: Motor ID run will occur at next start. Solution: 1. This is a informative warning no need to take any action. |
| AFF7 Autophasing | Cause: Autophasing will occur at next start. Solution: 1. This is a informative warning no need to take any action. |
| 2281 Calibration | Cause: Measured offset of output phase current measurement or difference between output phase U2 and W2 current measurement is too great (the values are updated during current calibration). Solution: 1. Try performing the current calibration again. 2. If problem not resolved then need to repair or replace drive. |
| 2310 Overcurrent | Cause: Output current has exceeded internal fault limit. In addition to an actual overcurrent situation, this fault may also be caused by an earth fault or supply phase loss. Solution: 1. Check motor load. 2. Check acceleration times in parameter group 23 Speed reference ramp (speed control), 26 Torque reference chain (torque control) or 28 Frequency reference chain (frequency control). 3. Also check parameters 46.01 Speed scaling, 46.02 Frequency scaling and 46.03 Torque scaling. 4. Check motor and motor cable (including phasing and delta/star connection). 5. Check there are no contactors opening and closing in motor cable. 6. Check that the start-up data in parameter group 99 Motor data corresponds to the motor rating plate. 7. Check that there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. 8. Check for an earth fault in motor or motor cables by measuring the insulation resistances of motor and motor cable. |
| 2330 Earth leakage | Cause: Drive has detected load unbalance typically due to earth fault in motor or motor cable. Solution: 1. Check there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. 2. Check for an earth fault in motor or motor cables by measuring the insulation resistances of motor and motor cable. 3. Try running the motor in scalar control mode if allowed. (See parameter 99.04 Motor control mode.) 4. After this if problem not resolved then need to repair or replace drive. |
| 2340 Short circuit | Cause: Short-circuit in motor cable(s) or motor. Aux code 0x0080 indicates that the state feedback from output phases does not match the control signals. Solution: 1. Check motor and motor cable for cabling errors. 2. Check there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. 3. Cycle the power to the drive. |
| 2381 IGBT overload | Cause: Excessive IGBT junction to case temperature. This fault protects the IGBT(s) and can be activated by a short circuit in the motor cable. Solution: 1. Check motor cable. 2. Check ambient conditions. 3. Check air flow and fan operation. 4. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 5. Check motor power against drive power. |
| 3130 Input phase loss | Cause: Intermediate circuit DC voltage is oscillating due to missing input power line phase or blown fuse. Solution: 1. Check input power line fuses. 2. Check for loose power cable connections. 3. Check for input power supply imbalance. |
| 3180 Charge relay lost | Cause: No acknowledgement received from charge relay. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 3181 Cross connection | Cause: Incorrect input power and motor cable connection (i.e. input power cable is connected to drive motor connection). Solution: 1. Check input power connections. |
| 3210 DC link overvoltage | Cause: Excessive intermediate circuit DC voltage. Solution: 1. Check that overvoltage control is on (parameter 30.30 Overvoltage control). 2. Check that the supply voltage matches the nominal input voltage of the drive. 3. Check the supply line for static or transient overvoltage. 4. Check deceleration time. Use coast-to-stop function (if applicable). 5. Retrofit drive with brake chopper and brake resistor. 6. Check that the brake resistor is dimensioned properly and the resistance is between acceptable range for the drive. |
| 3220 DC link undervoltage | Cause: Intermediate circuit DC voltage is not sufficient because of a missing supply phase, blown fuse or fault in the rectifier bridge. Solution: 1. Check supply cabling, fuses and switchgear. |
| 3280 Standby timeout | Cause: Automatic restart failed. Solution: 1. Check the condition of the supply (voltage, cabling, fuses, switchgear). |
| 3291 DC voltage difference | Cause: Difference in DC voltages between parallel connected inverter modules. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 3381 Output phase loss | Cause: Motor circuit fault due to missing motor connection (any of the three phases not connected). In scalar control mode, the drive detects fault only when the output frequency is above 10% of the motor nominal frequency. Solution: 1. Connect motor cable. 2. If the drive is in scalar mode and nominal current of the motor is less than 1/6 of the nominal output current of the drive, set parameter 31.19 Motor phase loss to No action. |
| 3385 Autophasing | Cause: Autophasing routine has failed. Solution: Try other autophasing modes (see parameter 21.13 Autophasing mode) if possible. |
| 4210 IGBT overtemperature | Cause: Estimated drive IGBT temperature is excessive. Solution: 1. Check air flow and fan operation. 2. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 3. Check motor power against drive power. 4. Check ambient conditions. |
| 4290 Cooling | Cause: Drive module temperature is excessive. Solution: 1. Check ambient temperature. If it exceeds , ensure that load current does not exceed derated load capacity of drive. 2. Check drive module cooling air flow and fan operation. 3. Check inside of cabinet and heatsink of drive module for dust pick-up. Clean whenever necessary. |
| 4310 Excess temperature | Cause: Power unit module temperature is excessive. Solution: 1. Check ambient conditions. 2. Check air flow and fan operation. 3. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 4. Check motor power against drive power. |
| 4380 Excess temperature difference | Cause: High temperature difference between the IGBTs of different phases. Solution: 1. Check the motor cabling. 2. Check cooling of drive module(s). |
| 42F1 IGBT temperature | Cause: Drive IGBT temperature is excessive. Solution: 1. Check ambient conditions. 2. Check air flow and fan operation. 3. Check heatsink fins for dust pick-up. 4. Check motor power against drive power. |
| 4981 External temperature 1 | Cause: Measured temperature 1 has exceeded fault limit. Solution: 1. Check the value of parameter 35.02 Measured temperature 1. 2. Check the cooling of the motor (or other equipment whose temperature is being measured). 3. Check the value of parameter 35.12 Temperature 1 fault limit. |
| 5080 Fan | Cause: Cooling fan is stuck or disconnected. Solution: 1. Check fan operation and connection. 2. Replace fan if faulty. |
| 5090 STO hardware failure | Cause: STO hardware diagnostics has detected hardware failure. Solution: There is an hardware issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 5091 Safe torque off | Cause: Safe torque off function is active, ie. safety circuit signal(s) connected to connector STO is broken during start or run. Solution: 1. Check safety circuit connections. 2. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 31.22 STO indication run/stop. |
| 5092 PU logic error | Cause: Power unit memory has cleared. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 5093 Rating ID mismatch | Cause: The hardware of the drive does not match the information stored in the memory. This may occur eg. after a firmware update. Solution: 1. Cycle the power to the drive. 2. You may have to be repeat this. 3. If fault not resolved after this then need to repair or replace drive. |
| 5681 PU communication | Cause: Communication errors detected between the drive control unit and the power unit. Solution: Check the connection between the drive control unit and the power unit. |
| 5682 Power unit lost | Cause: Connection between the drive control unit and the power unit is lost. Solution: Check the connection between the control unit and the power unit. |
| 5690 PU communication internal | Cause: Internal communication error. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 5691 Measurement circuit ADC | Cause: Measurement circuit fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 5692 PU board powerfail | Cause: Power unit power supply failure. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 5693 Measurement circuit DFF | Cause: Measurement circuit fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 5694 PU communication configuration | Cause: Version check cannot find a matching power unit FPGA logic. Solution: Update the FPGA logic of the power unit. |
| 5696 PU state feedback | Cause: State feedback from output phases does not match control signals. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 5697 Charging feedback | Cause: Charging feedback signal missing. Solution: Check the feedback signal coming from the charging system. |
| 5698 Unknown PU fault | Cause: The power unit logic generated a fault which is not known by software. Solution: Check the logic and software compatibility. |
| 6180 Internal SW error | Cause: Internal error. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 6181 FPGA version incompatible | Cause: Firmware and FPGA versions are incompatible. Solution: 1. Reboot the control unit (using parameter 96.08 Control board boot) or by cycling power. 2. After this same problem comes then need to repair or replace drive. |
| 6306 FBA A mapping file | Cause: Fieldbus adapter A mapping file read error. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive need to repair or replace drive. |
| 6481 Task overload | Cause: Internal fault. There is an internal issue in drive Solution: 1. Reboot the control unit (using parameter 96.08 Control board boot) or by cycling power. 2. After this same problem then need to repair or replace drive. |
| 6487 Stack overflow | Cause: Internal fault. There is an internal issue in drive Solution: 1. Reboot the control unit (using parameter 96.08 Control board boot) or by cycling power. 2. After this same problem then need to repair or replace drive. |
| 64A1 Internal file load | Cause: File read error. There is an internal issue in drive Solution: 1. Reboot the control unit (using parameter 96.08 Control board boot) or by cycling power. 2. After this same problem then need to repair or replace drive. |
| 64A2 Internal record load | Cause: Internal record load error. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 64A3 Application loading | Cause: Application file incompatible or corrupted. Note: This fault cannot be reset. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 64B2 User set fault | Cause: Loading of user parameter set failed because • requested set does not exist • set is not compatible with control program • drive was switched off during loading. Solution: Ensure that a valid user parameter set exists. Reload if uncertain. |
| 64E1 Kernel overload | Cause: Operating system error. Solution: 1. Reboot the control unit(using parameter 96.08 Control board boot) or by cycling power. 2. After this same problem then need to repair or replace drive. |
| 6581 Parameter system | Cause: Parameter load or save failed. Solution: Try forcing a save using parameter 96.07 Parameter save manually. Retry. |
| 65A1 FBA A parameter conflict | Cause: The drive does not have a functionality requested by PLC, or requested functionality has not been activated. Solution: 1. Check PLC programming. 2. Check settings of parameter groups 50 Fieldbus adapter (FBA) and 51 FBA A settings. |
| 6881 Text data overflow | Cause: Internal fault. Solution: 1. Reset the fault. 2. If fault not reset then there is an hardware or software issue in drive. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 6882 Text 32-bit table overflow | Cause: Internal fault. Solution: Reset the fault. If fault not reset then need to repair or replace drive. |
| 6883 Text 64-bit table overflow | Cause: Internal fault. Solution: Reset the fault. If fault not reset then need to repair or replace drive. |
| 6885 Text file overflow | Cause: Internal fault. Solution: Reset the fault. If fault not reset then need to repair or replace drive. |
| 7080 Option module comm loss | Cause: Communication between drive and option module (FEN-xx and/or FIO-xx) is lost. Solution: 1. Check that the option modules are properly seated in their slots. 2. Check that the option modules or slot connectors are not damaged. To pinpoint the problem, try installing the modules into different slots. |
| 7081 Panel port communication | Cause: Control panel or PC tool selected as active control location for drive has ceased communicating. Solution: 1. Check PC tool or control panel connection. 2. Check control panel connector. 3. Disconnect and reconnect the control panel. 4. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 49.05 Communication loss action. |
| 7121 Motor stall | Cause: Motor is operating in stall region because of e.g. excessive load or insufficient motor power. Solution: 1. Check motor load and drive ratings. 2. Check fault function parameters. |
| 7181 Brake resistor | Cause: Brake resistor broken or not connected. Solution: 1. Check that a brake resistor has been connected.heck the condition of the brake resistor. 2. Check the dimensioning of the brake resistor. |
| 7183 BR excess temperature | Cause: Brake resistor temperature has exceeded fault limit defined by parameter 43.11 Brake resistor fault limit. Solution: Stop drive. Let resistor cool down. Check resistor overload protection function settings (parameter group 43 Brake chopper). Check fault limit setting, parameter 43.11 Brake resistor fault limit. Check that braking cycle meets allowed limits. |
| 7184 Brake resistor wiring | Cause: Brake resistor short circuit or brake chopper control fault. Solution: 1. Check brake chopper and brake resistor connection. 2. Ensure brake resistor is not damaged. |
| 7191 BC short circuit | Cause: Short circuit in brake chopper IGBT. Solution: 1. Ensure brake resistor is connected and not damaged. 2. Check the electrical specifications of the brake resistor. |
| 7192 BC IGBT excess temp | Cause: Brake chopper IGBT temperature has exceeded internal fault limit. Solution: 1. Let chopper cool down.Check for excessive ambient temperature. 2. Check for cooling fan failure. 3. Check for obstructions in the air flow. 4. Check the dimensioning and cooling of the cabinet. 5. Check that braking cycle meets allowed limits. 6. Check that drive supply AC voltage is not excessive. |
| 71A2 Mechanical brake closing failed | Cause: Mechanical brake control fault. Activated e.g., if brake acknowledgment is not as expected during brake closing. Solution: 1. Check mechanical brake connection. 2. Check mechanical brake settings in parameter group 44 Mechanical brake control. 3. Check that the acknowledgment signal matches the actual status of the brake. 4. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 44.17 Brake fault function |
| 71A3 Mechanical brake opening failed | Cause: Mechanical brake control fault. Activated e.g. if brake acknowledgment is not as expected during brake opening. Solution: 1. Check mechanical brake connection. 2. Check mechanical brake settings in parameter group 44 Mechanical brake control. 3. Check that acknowledgment signal matches actual status of brake. 4. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 44.17 Brake fault function |
| 71A5 Mechanical brake opening not allowed | Cause: Open conditions of mechanical brake cannot be fulfilled (e.g., the brake has been prevented from opening by parameter 44.11). Solution: 1. Check mechanical brake settings in parameter group 44 Mechanical brake control (especially 44.11). 2. Check that the acknowledgment signal (if used) matches the actual status of the brake. |
| 7301 Motor speed feedback | Cause: No motor speed feedback received. Encoder speed differs too much from internal speed estimate. Solution: 1. Check the parameter 90.41 setting and the actual source selected. 2. Check electrical connection of the encoder and pulse sin/cos nr. 3. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 90.45 Motor feedback fault |
| 7310 Overspeed | Cause: Motor is turning faster than highest allowed speed due to incorrectly set minimum/maximum speed, insufficient braking torque or changes in load when using torque reference. Solution: 1. Check minimum/maximum speed settings, parameters 30.11 Minimum speed and 30.12 Maximum speed. 2. Check adequacy of motor braking torque. 3. Check applicability of torque control. 4. Check need for brake chopper and resistor(s). |
| 7380 Encoder internal | Cause: Internal fault. Solution: There is an hardware or software issue in drive or encoder/encoder board. Need to repair or replace drive. |
| 7381 Encoder 1 | Cause: Encoder 1 feedback fault. Solution: 1. If fault appears during first start-up before encoder feedback is used: – Check cable between encoder and encoder interface module (FEN-xx) and order of connector signal wires at both ends of cable. 2. If fault appears after encoder feedback has already been used or during drive : – Check that encoder connection wiring or encoder is not damaged. – Check that encoder interface module (FEN-xx) connection or module is not damaged. – Check earthings (when disturbances are detected in communication between encoder interface module and encoder). 3. For more information on encoders, see parameter groups 90 Feedback selection, 91 Encoder module settings, 92 Encoder 1 configuration and 93 Encoder 2 configuration. |
| 7391 Encoder 2 | Cause: Encoder 2 feedback fault. Solution: 1. If fault appears during first start-up before encoder feedback is used: – Check cable between encoder and encoder interface module (FEN-xx) and order of connector signal wires at both ends of cable. 2. If fault appears after encoder feedback has already been used or during drive : – Check that encoder connection wiring or encoder is not damaged. – Check that encoder interface module (FEN-xx) connection or module is not damaged. – Check earthings (when disturbances are detected in communication between encoder interface module and encoder). 3. For more information on encoders, see parameter groups 90 Feedback selection, 91 Encoder module settings, 92 Encoder 1 configuration and 93 Encoder 2 configuration. |
| 73A0 Speed feedback configuration | Cause: Speed feedback configuration incorrect, eg. an encoder that is not present is selected as the feedback interface. Solution: 1. Check the feedback source selection parameters in group 90 Feedback selection. 2. In case the source is an encoder interface, check parameter settings in groups 91 Encoder module settings, 92 Encoder 1 configuration and 93 Encoder 2 configuration. |
| 73A1 Load feedback | Cause: No load feedback received. Solution: 1. Check the setting of parameter 90.51 Load feedback selection, and the actual source selected. 2. In case the source is an encoder interface, check parameter settings in groups 91 Encoder module settings, 92 Encoder 1 configuration and 93 Encoder 2 configuration. |
| 7510 FBA A communication | Cause: Cyclical communication between drive and fieldbus adapter module A or between PLC and fieldbus adapter module A is lost. Solution: 1. Check status of fieldbus communication. 2. Check settings of parameter groups 50 Fieldbus adapter (FBA), 51 FBA A settings, 52 FBA A data in and 53 FBA A data out. 3. Check cable connections. 4. Check if communication master is able to communicate. 5. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 50.02 FBA A comm loss function. Note: If the module has been changed from FieldBus (for example FPBA) to some other option module (for example BMIO), the factory defaults need to be applied (see parameter 96.06). |
| 80B0 Signal supervision | Cause: Fault generated by the signal supervision 1 function. Solution: 1. Check the source of the fault (parameter 32.07 Supervision 1 signal). 2. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 32.06 Supervision 1 action |
| 9081 External fault 1 | Cause: Fault in external device 1. Solution: Check the external device. Check setting of parameter 31.01 External event 1 source. This is a Programmable fault: check parameter 31.01 External event 1 source 31.02 External event 1 type. |
| FA81 Safe torque off 1 | Cause: Safe torque off function is active, ie. STO circuit 1 is broken. Solution: Check safety circuit connections. |
| FA82 Safe torque off 2 | Cause: Safe torque off function is active, ie. STO circuit 2 is broken. Solution: Check safety circuit connections. |
| FF61 ID run | Cause: Motor ID run was not completed successfully. Solution: 1. Check the nominal motor values in parameter group 99 Motor data. 2. Check that no external control system is connected to the drive. 3. Cycle the power to the drive (and its control unit, if powered separately). 4. Check that no operation limits prevent the completion of the ID run. Restore parameters to default settings and try again. 5. Check that the motor shaft is not locked. |
| FF81 FB A force trip | Cause: A fault trip command has been received through fieldbus adapter A. Solution: Check the fault information provided by the PLC. |
| FF82 FB B force trip | Cause: A fault trip command has been received through fieldbus adapter B. Solution: 1. Check the fault information provided by the PLC. |
| FF8E EFB force trip | Cause: A fault trip command has been received through the embedded fieldbus interface. Solution: Check the fault information provided by the PLC. |
| 2391 BU current difference | Cause: AC phase current difference between parallel-connected inverter modules is excessive. Solution: 1. Check motor cabling. 2. Check there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. |
| 2392 BU earth leakage | Cause: Total earth leakage of inverter modules is excessive. Solution: 1. Check there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in motor cable. 2. Measure insulation resistances of motor cables and motor. |
| 2E01 Earth leakage | Cause: IGBT supply unit has detected an earth fault. Solution: 1. Check AC fuseheck for earth leakages. 2. Check supply cabling. 3. Check power modules. 4. Check there are no power factor correction capacitors or surge absorbers in supply cable. |
| 3000 Invalid voltage chain datapoints | Cause: Parametrization of the speed/torque limitation curve (in the DC voltage reference chain) are inconsistent. Solution: 1. Check that the speed points of the curve (defined by 29.70…29.79) are in increasing order. |
| 3E00 Input phase loss | Cause : Input phase loss comes when input phase loss detected by the IGBT bridge. A 3E00 fault code in your ABB ACS880 drive indicates an input phase loss. This means the drive isn’t detecting all three phases of the incoming AC power supply. Solution: 1. Check the auxiliary code. 2. Check the source of the fault corresponding to the code: 1: Phase A, 2: Phase B, 4: Phase C, 8: Phase cannot be detected. 3. Check the AC fuses. 4. Check for input power supply imbalance. |